South Beach Diet Phase 1 Avocado: Unlocking the creamy, healthy heart of this popular weight-loss plan. Phase 1 of the South Beach Diet is known for its strict limitations, but avocados offer a surprisingly delicious and nutritious way to stay full and satisfied while shedding those extra pounds. This guide dives deep into how avocados fit into the Phase 1 framework, exploring their nutritional benefits, recipe ideas, and potential caveats.
Prepare to discover a new appreciation for this versatile fruit and how it can power your weight-loss journey.
We’ll cover everything from the fundamental principles of the South Beach Diet Phase 1 and the specific role avocados play within its guidelines to practical recipe examples and potential health benefits. We’ll also address common concerns and provide tips for safe and effective avocado integration into your diet. Get ready to optimize your South Beach Diet experience with the power of the avocado.
South Beach Diet Phase 1 Overview
South Beach Diet Phase 1 is the initial, crucial stage of this popular weight-loss plan. Its primary goal isn’t just about shedding pounds, but about re-training your body to prioritize healthy fuel sources and manage blood sugar levels effectively. This phase emphasizes a low-glycemic approach, focusing on foods that release energy slowly and prevent those frustrating energy crashes and cravings often associated with rapid blood sugar spikes.
The restrictions in Phase 1 are temporary, designed to jumpstart the weight loss process and establish healthy eating habits that can be maintained long-term.The South Beach Diet Phase 1 focuses on eliminating refined carbohydrates and unhealthy fats to promote healthy weight loss and improved metabolic function. This initial phase is designed to be a short-term jumpstart, typically lasting two weeks, before transitioning to the more flexible phases.
Permitted and Restricted Food Groups in Phase 1
Phase 1 of the South Beach Diet carefully curates the types of foods you can and cannot eat. Understanding this distinction is vital for successful implementation. This careful selection of foods is key to managing blood sugar and suppressing hunger, contributing to sustainable weight loss.
- Permitted Foods: Lean proteins (fish, poultry, beans, tofu), healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil), non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, peppers), and limited amounts of whole grains (in moderation).
- Restricted Foods: Sugary drinks, processed foods, refined grains (white bread, pasta), most fruits (except berries in limited quantities), and unhealthy fats (trans fats, saturated fats from red meat).
Rationale Behind Dietary Restrictions in Phase 1
The restrictions in Phase 1 aren’t arbitrary; they’re based on the understanding of how different foods affect blood sugar and insulin levels. By eliminating refined carbohydrates and unhealthy fats, the diet aims to minimize blood sugar spikes and insulin resistance. This approach helps regulate appetite, reduces cravings, and promotes fat burning.The elimination of refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and sugary drinks, is crucial because these foods are rapidly digested, leading to significant blood sugar spikes followed by equally dramatic crashes.
These fluctuations contribute to increased hunger and cravings, hindering weight loss efforts. Similarly, restricting unhealthy fats minimizes the intake of calories that are easily stored as body fat and contribute to cardiovascular issues. The emphasis on lean proteins and healthy fats ensures the body receives the necessary nutrients while supporting satiety and metabolic function. This controlled approach helps establish a sustainable pattern of healthy eating, paving the way for long-term weight management success.
Avocado Consumption and Weight Management: South Beach Diet Phase 1 Avocado

The South Beach Diet Phase 1 emphasizes the consumption of healthy fats, and avocados stand out as a particularly beneficial choice for weight management during this initial phase. Their unique nutritional profile, coupled with their impact on satiety and blood sugar control, contributes to a sustainable and effective approach to weight loss.Avocados offer a unique combination of nutrients that support weight loss goals.
Unlike many other fruits, avocados are relatively high in healthy fats, specifically monounsaturated fats, which are associated with improved cardiovascular health and potentially aiding in weight management. These fats promote satiety, meaning they help you feel fuller for longer, reducing overall calorie intake. Furthermore, the fiber content in avocados contributes to this feeling of fullness and aids in digestive regularity.
Avocado Nutritional Profile Compared to Other Phase 1 Foods
The nutritional profile of avocados distinguishes them from other Phase 1-approved foods. While many Phase 1 foods are lean protein sources or low-carbohydrate vegetables, avocados offer a significant amount of healthy fats alongside fiber and essential nutrients. For instance, a medium-sized avocado contains approximately 322 calories, 29 grams of fat (mostly monounsaturated), 14 grams of fiber, and 10 grams of carbohydrates.
This contrasts with foods like chicken breast (primarily protein and minimal fat) or leafy greens (low in calories and fat, high in fiber). This rich nutrient profile, while calorie-dense, supports feelings of fullness and provides sustained energy throughout the day, potentially preventing overeating. A direct comparison would show avocados being higher in calories and fat than lean proteins, but significantly higher in fiber than most vegetables permitted in Phase 1.
This difference is crucial to understand when considering its role in weight management.
Avocado’s Contribution to Satiety and Blood Sugar Control
Avocados contribute significantly to satiety and blood sugar control, both crucial for successful weight loss. The high fiber content slows down digestion, leading to a prolonged feeling of fullness. This reduces the likelihood of snacking between meals or overeating at your next meal. Moreover, the healthy fats in avocados help to regulate blood sugar levels, preventing the energy crashes and subsequent cravings that often lead to overconsumption of less healthy foods.
This stable blood sugar prevents the insulin spikes and subsequent dips associated with refined carbohydrates, further aiding in weight management. Studies have shown that incorporating foods rich in healthy fats and fiber, like avocados, can lead to increased feelings of fullness and improved appetite regulation, ultimately contributing to a lower overall caloric intake. This effect is particularly beneficial during Phase 1 of the South Beach Diet, which emphasizes a controlled carbohydrate intake.
Potential Health Benefits of Avocados in Phase 1
Avocados, often overlooked in weight-loss plans, offer a surprising array of health benefits that align perfectly with the principles of the South Beach Diet Phase 1. Beyond their role in satiety and healthy fat intake, avocados contribute significantly to overall well-being through their rich nutrient profile. This section will explore these additional benefits, focusing on research-backed evidence supporting their positive impact on cardiovascular health and beyond.Avocados are a nutritional powerhouse, providing more than just healthy fats.
Their contribution to cardiovascular health, in particular, is noteworthy within the context of the South Beach Diet’s emphasis on heart-healthy eating.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits of Avocados
Studies suggest that regular avocado consumption can positively impact various cardiovascular risk factors. For instance, research published in theJournal of the American Heart Association* indicates that including avocados in a diet can improve lipid profiles. Specifically, studies have shown that avocados can increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), often referred to as “good” cholesterol, while simultaneously lowering levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol.
This beneficial effect on cholesterol levels is attributed to the unique blend of monounsaturated fats, fiber, and other bioactive compounds found in avocados. Furthermore, avocados contain potassium, a mineral essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Adequate potassium intake is crucial for counteracting the negative effects of sodium on blood pressure, a key risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Avocado Nutrient Profile and Their Roles in Overall Health
A visual representation of avocado’s key nutrients could be a pie chart. The largest segment would represent healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), highlighting their role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and providing sustained energy. A significant portion would be dedicated to fiber, emphasizing its contribution to digestive health, blood sugar regulation, and satiety. Smaller segments would represent potassium (for blood pressure regulation), vitamin K (for blood clotting and bone health), vitamin C (an antioxidant), and folate (essential for cell growth and development).
Each segment would be clearly labeled with the nutrient’s name and a concise description of its primary health benefit. For instance, the potassium segment could include a small note indicating its role in blood pressure regulation. The overall image would convey the comprehensive nutritional value of avocados, demonstrating their contribution to various aspects of health beyond weight management.
Avocado Recipes for South Beach Diet Phase 1
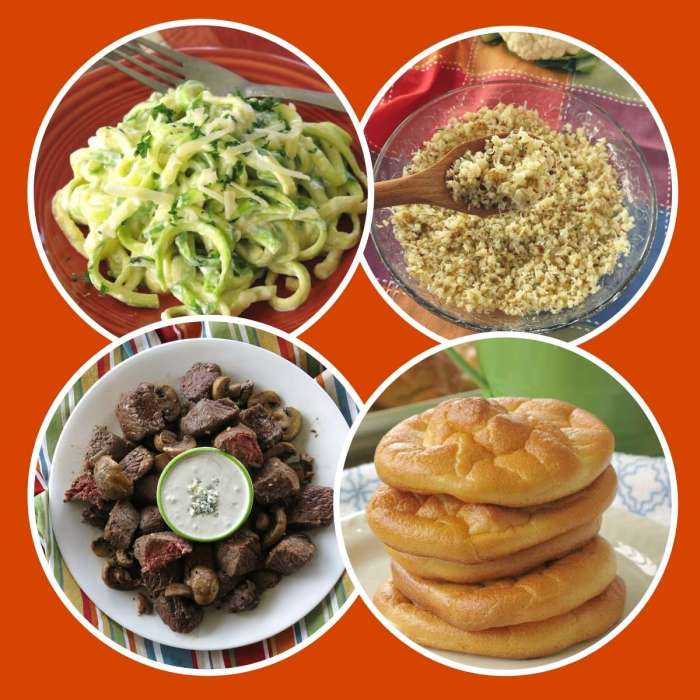

South Beach Diet Phase 1 emphasizes healthy fats and limits sugars and refined carbohydrates. Avocados, rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber, fit perfectly into this plan. These recipes demonstrate how to incorporate avocados into various meals, keeping in mind the Phase 1 restrictions. Each recipe is designed to be both delicious and compliant.
Quick Avocado Breakfast
This recipe takes only five minutes to prepare, making it ideal for busy mornings.
Ingredients:
- 1/2 ripe avocado, mashed
- 1/4 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1/4 teaspoon vanilla extract
- Pinch of salt
Instructions:
Combine all ingredients in a small bowl and mix well. Enjoy immediately. The chia seeds add a boost of fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. The almond milk provides creaminess without added sugars.
Speedy Avocado Lunch
This simple salad can be prepared in under 10 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 1 ripe avocado, diced
- 1 cup mixed greens
- 1/2 cup cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1/4 cup crumbled feta cheese (optional, check for Phase 1 compliance)
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 1 tablespoon lemon juice
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
Combine the mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, and avocado in a bowl. In a separate small bowl, whisk together the olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper. Pour the dressing over the salad and toss gently. Add feta cheese if desired. This recipe provides healthy fats, fiber, and a refreshing taste.
Hearty Avocado Dinner
This recipe requires slightly more preparation time but offers a satisfying and flavorful meal.
Ingredients:
- 1 ripe avocado, sliced
- 4 ounces grilled chicken breast, sliced
- 1 cup cauliflower rice
- 1/4 cup chopped red onion
- 2 tablespoons chopped cilantro
- 1 tablespoon lime juice
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
Cook the cauliflower rice according to package directions. In a bowl, combine the cauliflower rice, grilled chicken, red onion, and cilantro. Top with avocado slices. Drizzle with lime juice and season with salt and pepper. This dinner provides lean protein, healthy fats, and fiber, all crucial elements of a balanced South Beach Diet Phase 1 meal.
Considerations and Precautions
While avocados offer numerous benefits and can be a delicious addition to the South Beach Diet Phase 1, it’s crucial to approach their consumption with awareness. Relying too heavily on any single food, even a healthy one like the avocado, can lead to nutritional imbalances and other potential issues. This section addresses potential drawbacks and provides guidance for safe and effective avocado integration.
The high fat content of avocados, while mostly beneficial monounsaturated fats, needs careful consideration. Overconsumption can lead to exceeding daily caloric goals, hindering weight loss progress. Furthermore, while avocados are rich in fiber, excessive intake could cause digestive discomfort for some individuals, such as bloating or diarrhea. Finally, certain potential interactions with medications or pre-existing health conditions need to be addressed.
Avocado Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
Avocados contain compounds that can interact with certain medications, primarily those affecting blood clotting. For example, individuals taking blood thinners like warfarin should monitor their INR levels closely when significantly increasing avocado consumption, as avocados may enhance the anticoagulant effect. Similarly, people with known allergies to latex should exercise caution, as some individuals allergic to latex may also experience allergic reactions to avocados due to cross-reactivity.
Consulting with a healthcare professional before significantly altering avocado intake, especially if on medication or with pre-existing conditions, is highly recommended. This proactive approach ensures safe and effective dietary management.
Avocado Portion Control within the South Beach Diet Phase 1, South Beach Diet Phase 1 Avocado
Maintaining appropriate portion sizes is vital to reaping the benefits of avocados without jeopardizing the South Beach Diet’s goals. A single medium-sized avocado (approximately 200 grams) contains roughly 322 calories and a significant amount of healthy fats. Therefore, incorporating one-half to one whole avocado per day, depending on individual caloric needs and activity levels, is a reasonable guideline.
It’s crucial to remember that avocados should complement, not dominate, the overall diet. Including a variety of other Phase 1-approved foods, such as lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats from other sources, ensures a balanced and nutritionally complete meal plan. Regularly monitoring weight and adjusting avocado intake as needed will further optimize the results.
Mastering the South Beach Diet Phase 1 can feel challenging, but incorporating avocados can significantly enhance your experience. From their impressive nutritional profile and contribution to satiety to their versatility in various recipes, avocados offer a potent tool for weight management and overall well-being. Remember mindful portion control and awareness of potential interactions, and you’ll be well on your way to enjoying the delicious benefits of this superfood while successfully navigating the initial phase of the South Beach Diet.
The journey to a healthier you is paved with delicious, informed choices – and avocados are a fantastic place to start.